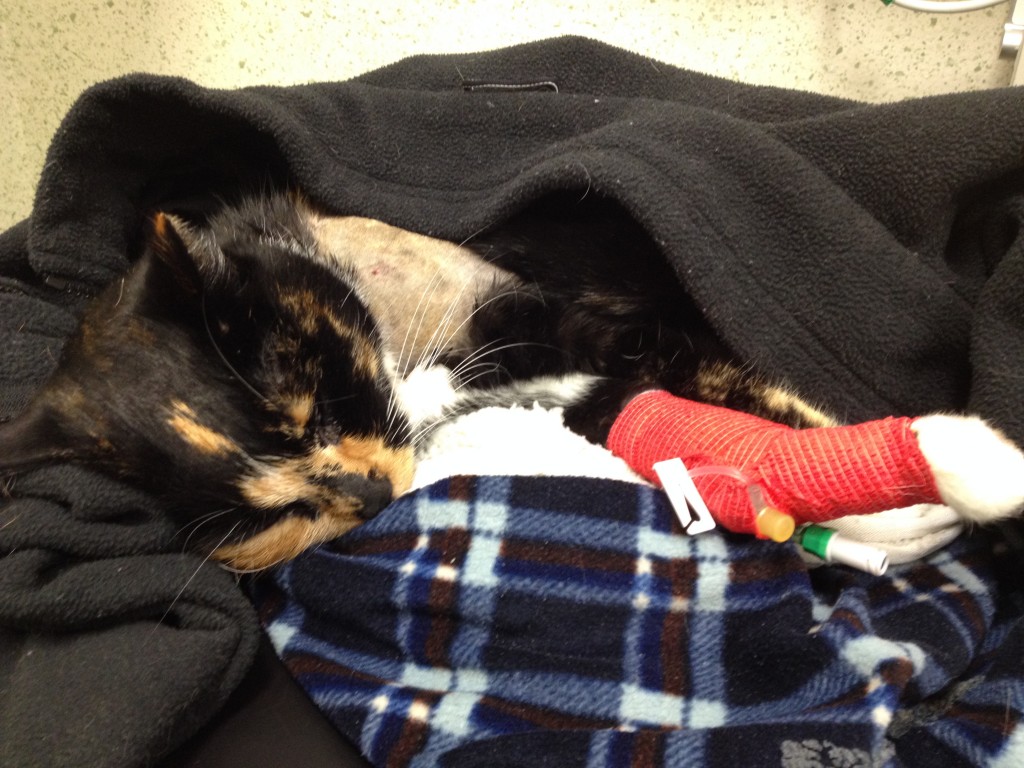
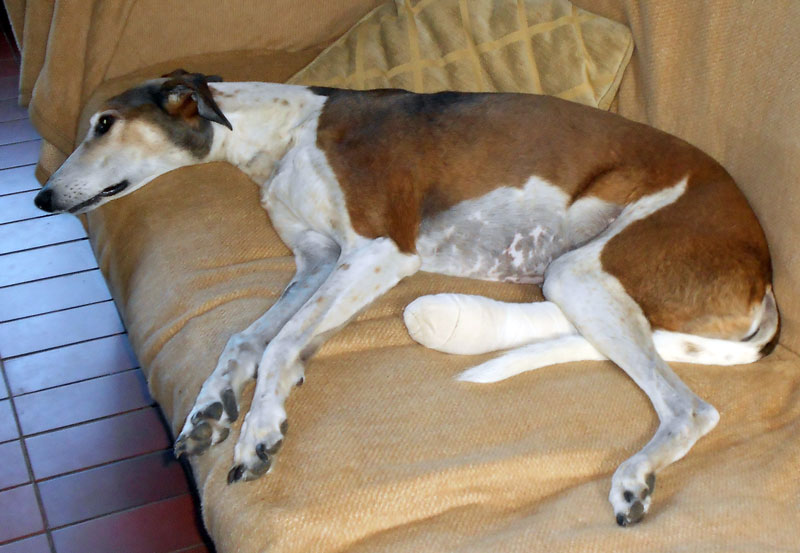
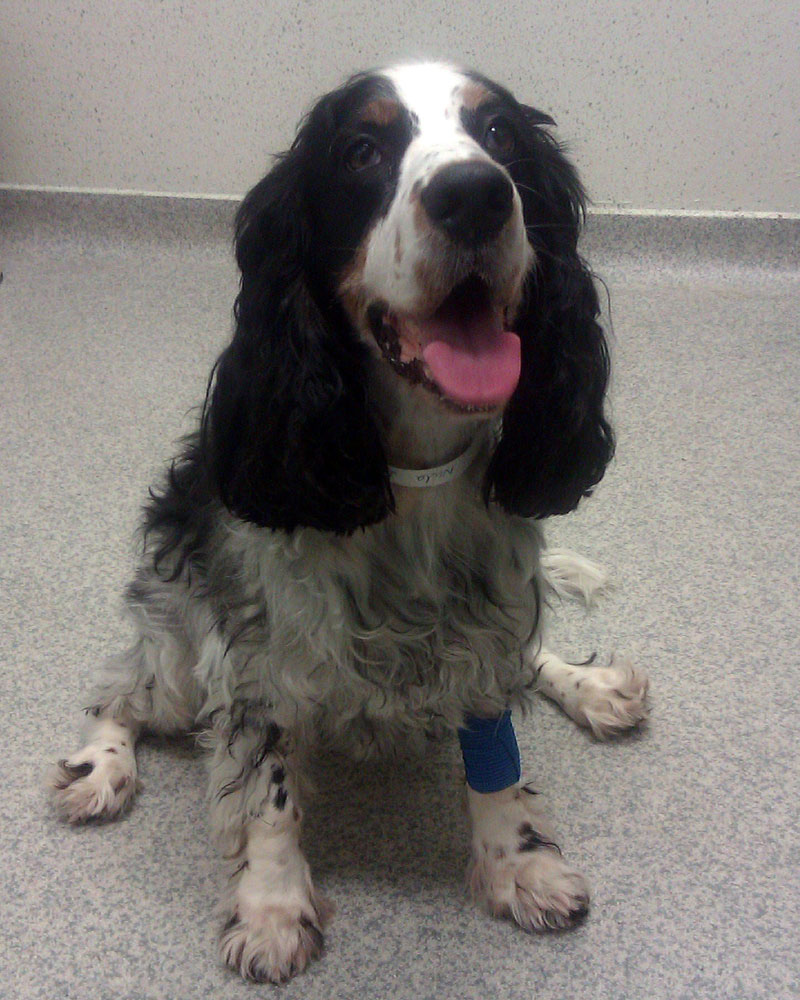
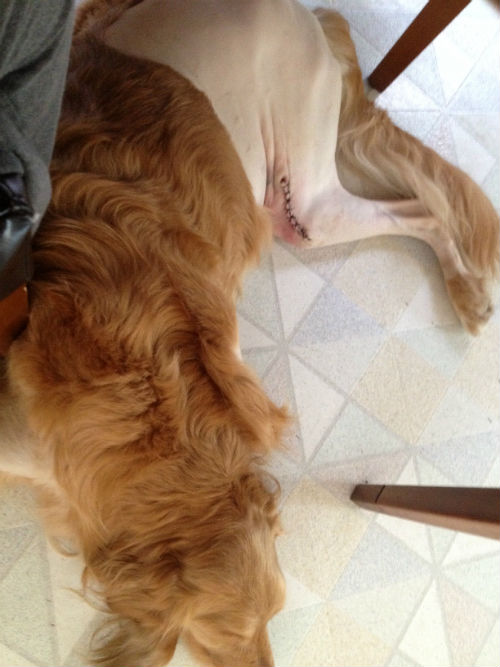
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) is a life-threatening blood condition requiring emergency treatment. Abnormal clotting AND bleeding occur in the body simultaneously and it is very difficult to treat, even with an experienced emergency team on hand. DIC is secondary to (a consequence of) another serious condition or combination of conditions such as AIHA. Early detection of signs of DIC will help the outcome, but it is very difficult to diagnose in the initial stages.
DIC = uncontrolled THROMBIN and PLASMIN. Excess thrombin leads to clotting, excess plasmin leads to bleeding.
Initially, a large production of thrombin causes widespread clotting. DIC patients will often have low platelet counts, an increase in clotting times on PT (prothrombin time & PTT (partial prothrombin time) tests, presence of fibrin degradation products , one of which is called called D-DIMER, reduced fibrinogen levels in the blood may also be an indicator. These tests are looking for evidence of clot breakdown. Unfortunately, there is no single test to diagnose DIC. A type of abnormal shaped red blood cells called Keratocytes or horn cells – shaped like a spindle or a half moon – are indicators for DIC on a blood smear.
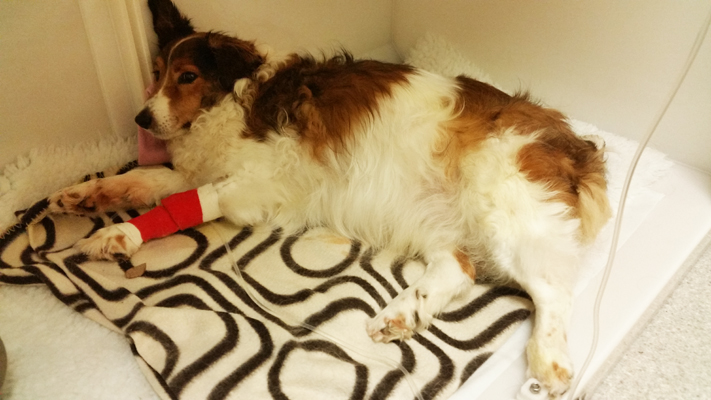
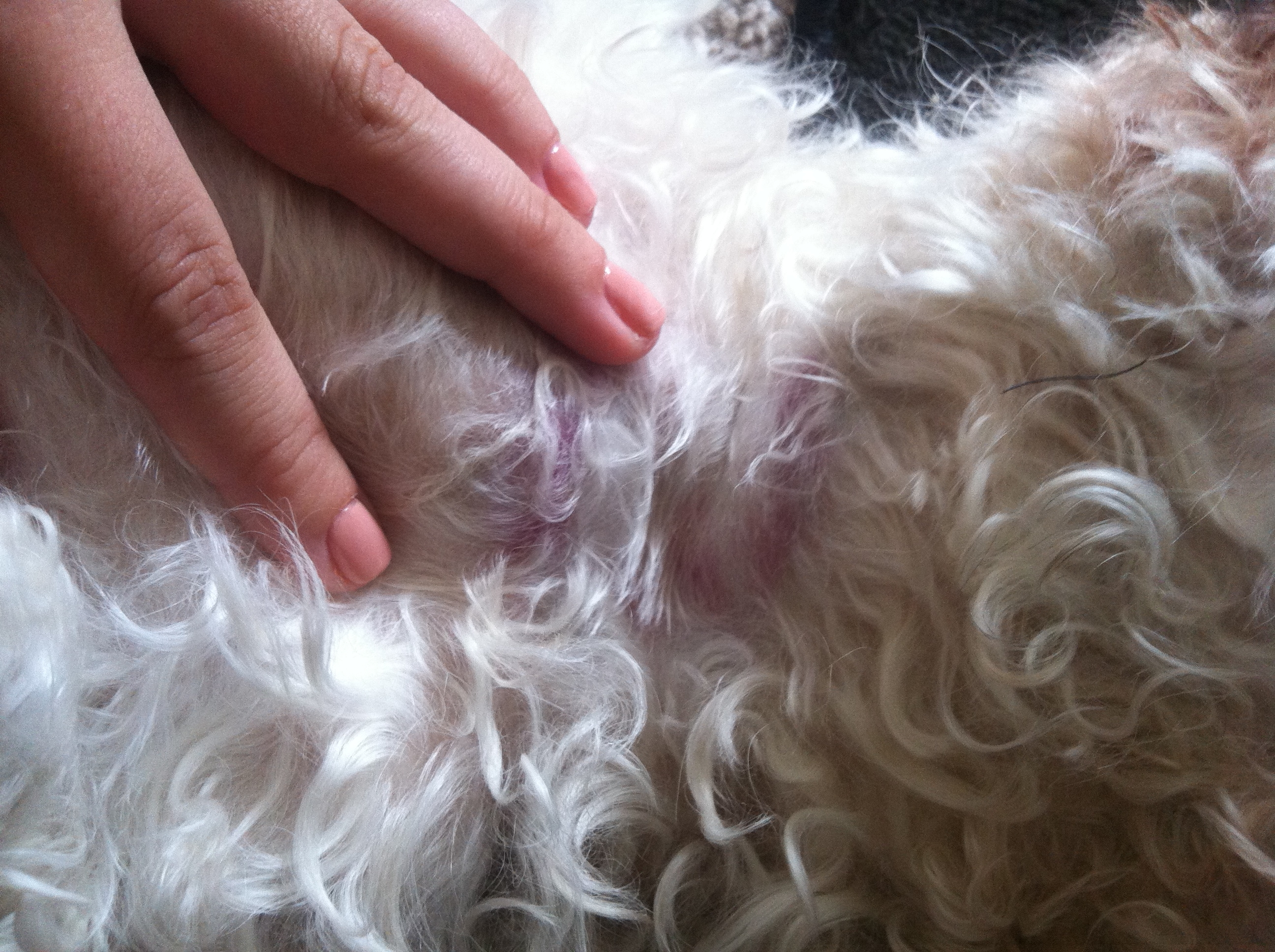
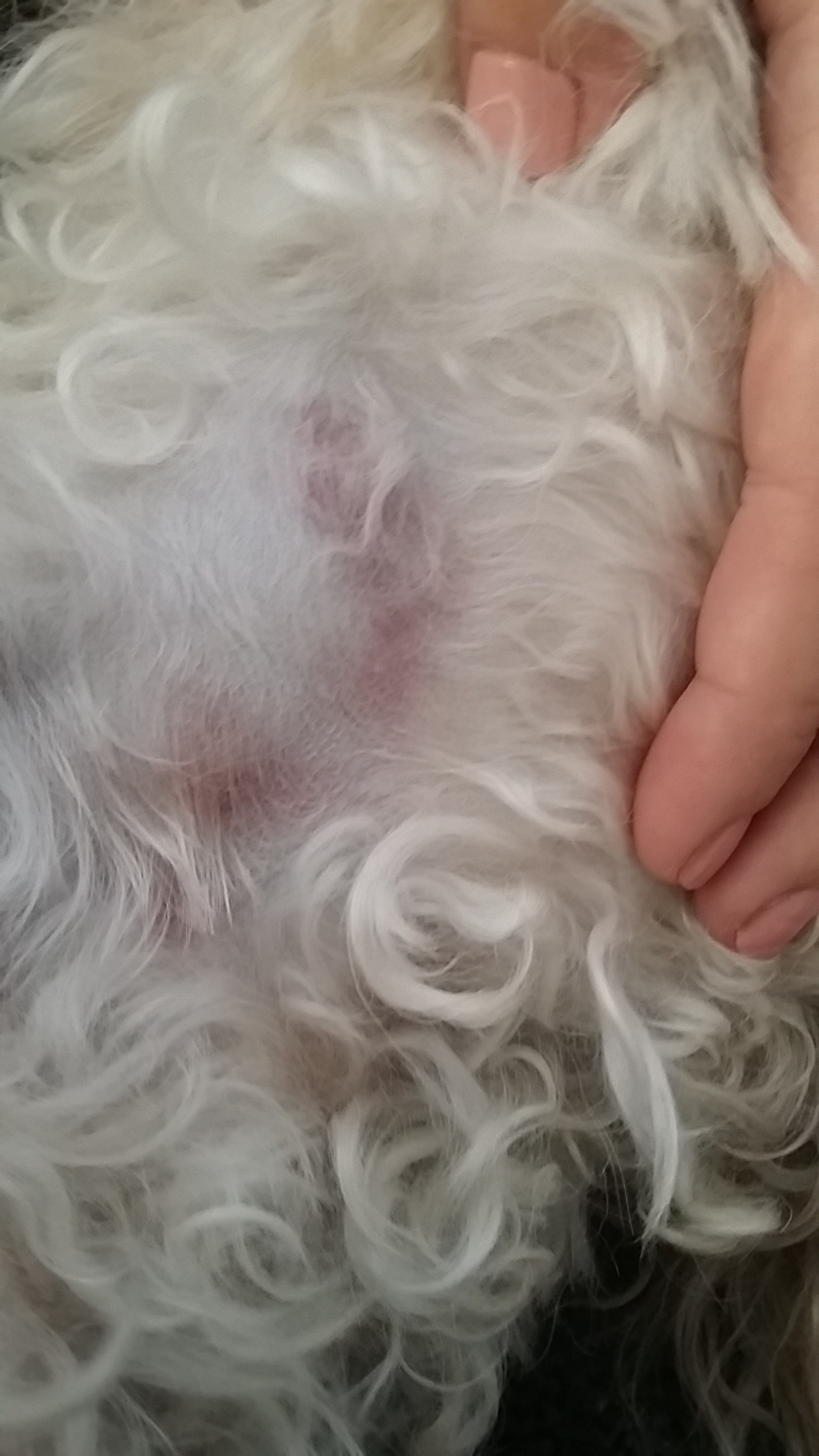
Physical signs: Evidence of bleeding such as bruising & petechiae, bleeding from the site where a blood sample was taken, bleeding from orifices such as the nose, mouth or anus, bleeding from gums can indicate DIC.
Conditions which may be associated with DIC include AIHA/IMHA, IMT, pancreatitis, hemangiosarcoma, massive & overwhelming infections, reaction to blood transfusion, heartworm, bebesiosis, burns, some neoplasia, Cushings Disease, snake bite, heatstroke, electrocution, hepatitis, endocarditis, severe liver failure, injury or trauma due to being crushed (e.g. car accident), glomerular disease (a type of kidney disease), protein losing enteropathy.
Treatment is controversial & relies on restoration of circulation to normal levels by IV fluids to perfuse organs. Plasma transfusions (pretreated with heparin) are used to replace the proteins required for blood clotting. Oxygen is given to maintain oxygenation levels. Finding & treating the cause of DIC is vitally important, including adminstration of antibiotics & any necessary surgery.
« Back to Glossary Index