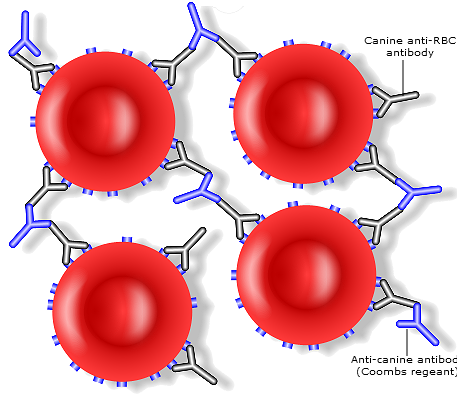
The Coombs Test is used to detect canine-specific antibodies against red blood cells. It is used to support the diagnosis of IMHA when tests have ruled out most other causes of anemia but autoagglutination is not seen. A positive result is not necessarily diagnostic for IMHA as other diseases can also show a positive result. About 65-75% of dogs with IMHA have a positive Coombs Test. False negatives are also frequently reported in up 42% of dogs with IMHA. If combined with a blood smear examination the reliability can be improved.
Your vet will generally perform the more sensitive Direct Coombs Test (DAT). This tests the activity of the antibodies at different temperatures.
Antibodies with high activity at about 98°F are called warm autoantibodies. Cold autoantibodies have high activity around 39°F.
Dogs with Cold AIHA will have a higher autoantibody activity when they are hypothermic. So RBC’s in the limbs would become susceptible to the antibodies. When they return to the warmer body core the RBC’s are destroyed. Your dog may have one or both types of autoantibodies. Both types in your dog will be called mixed-type AIHA.
Also known as antiglobulin test.